What is Malware? Explanation of Infection Risks, Typical Types, Intrusion Routes, and Preventive Measures

In recent years, an increasing number of companies are adopting remote work. In remote work, employees need to access the company’s internal systems from the outside, making the strengthening of security measures an important issue. In particular, ‘malware’ is a threat to IT tools such as PCs and smartphones, and it is important to understand its characteristics and take effective measures.
This article explains the overview of malware, the symptoms and risks of infection, and the typical types of malware. We will also check the main intrusion and infection routes of malware, how to prevent malware infection, and effective security tools to create an environment where you can proceed with your work without any problems.
Table of Contents
- What is Malware?
- Symptoms and Risks of Malware Infection
- Typical Types of Malware
- Virus
- Worm
- Trojan Horse
- Spyware
- Ransomware
- Malware Intrusion Routes
- How to Prevent Malware Infection
- Summary
1. What is Malware?
Malware is a coined word combining the two words ‘malicious’ and ‘software.’ Malware is generally software created for the purpose of illegally performing harmful or annoying actions for the user.
In the early days of computers, many malware programs were developed for prankish purposes, such as ‘to surprise infected users,’ and the direct damage was not so great. However, as computers became more widespread, annoying damage to users increased, such as ‘harmful effects on operation’.
Today, the mainstream is malware developed for the purpose of leaking information without the user’s knowledge. Because methods that are difficult to detect and difficult to notice infection are used, security tools should be used to remove malware before it invades the device.
1-1. Symptoms and Risks of Malware Infection
If you notice the following symptoms on your computer, it is highly likely that you have been attacked by malware.
■ Typical symptoms of malware infection
- Computer performance slows down
- Computer starts up or shuts down without permission
- A large number of advertisements are displayed
- Browser behavior becomes strange
- There is a program that you don’t recognize
- A message appears warning that you are infected with a virus and prompting you to purchase or pay for something

If left unattended in an infected state, there is a risk of damage such as ‘account hijacking,’ ‘theft of financial information,’ ‘automatic data deletion,’ and ‘mass distribution of spam emails.’ If you notice any unusual behavior on your computer, suspect a malware infection and take action.
2. Typical Types of Malware
There are many types of malware, and the content of malware continues to evolve with the development of computers. In order to protect your computer from various malware, it is important to understand the general types and types of malware.
■ Typical Malware
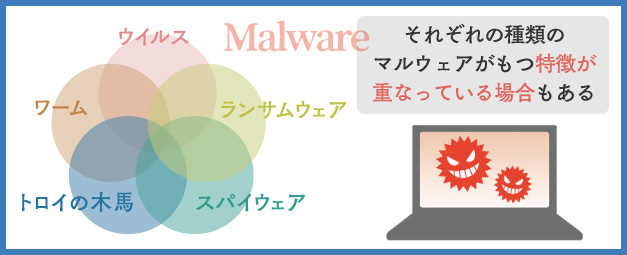
Here, we will explain the characteristics and differences in properties of five typical types of malware, and the risks of infection.
2-1. Virus
A ‘virus (computer virus)’ is malware that partially rewrites the program of a file or app that is the host to tamper with its own code and self-replicates.
When a file or app infected with a virus is executed, the virus multiplies along with harmful actions, but in many cases, the virus multiplication cannot be seen with the naked eye. Be careful that there is a high risk of spreading the virus without knowing it.
2-2. Worm
‘Worm’ means ‘worm (parasite)’ and refers to malware that can operate independently and also self-replicate. Depending on the type of worm, some have high infection power that can infect millions of computers just by connecting to the internet, so caution is required.
Note that worms are malware that is easy to detect infection. Therefore, it is not used so much in modern times, where the mainstream is the method of secretly infecting. However, it is important to note that there are worms that are still used in recent years, and that measures are difficult to take because of their high infection power.
2-3. Trojan Horse
A ‘Trojan horse’ is malware that infiltrates the computer by disguising itself as a harmless file or app, and performs malicious actions according to the intentions of the creator or attacker. It is named after the ‘Trojan horse’ that appears in Greek mythology.
Trojan horses tend to take time to notice infection because they are often disguised as general files. It does not have a self-replication function or a diffusion function, but it has functions such as stealing personal information and creating a backdoor that allows unauthorized access at any time, making it a very dangerous malware.
2-4. Spyware
‘Spyware’ is an illegal program that collects user behavior and personal information and sends it to a completely different location. It is said that spyware is often installed together when users download free software.
Spyware is not disguised like a Trojan horse. However, because it is malware intended to steal information, it does not operate publicly and is difficult to detect.
2-5. Ransomware
Ransomware is a coined word combining ‘ransom’ and ‘software.’ When a device is infected with ransomware, files are encrypted and become unusable, and a message appears demanding a ‘ransom’ to restore this state.
It is said to be very difficult to restore files damaged by ransomware to their original state. Even if you pay the ‘ransom’ in the message displayed on the computer screen, there is no guarantee that the data can be restored.
3. Malware Intrusion Routes
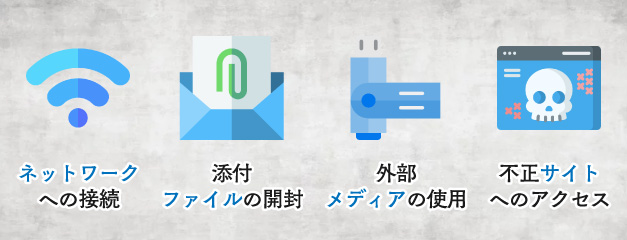
There are many malware intrusion patterns. Here, we will introduce typical routes for malware to illegally intrude.
- Connecting to a network
If you connect to a network such as the Internet while leaving vulnerabilities in your OS or apps, there is a risk of being infected with malware (mainly worms).
- Opening files attached to messages
Opening files attached to emails can lead to infection with malware such as viruses, worms, and Trojan horses.
- Use of external media
If a virus is hidden in external media/external memory such as USB memory, there is a risk of infection by using it on a computer.
- Access to illegal websites
By connecting to and browsing sites that have been tampered with by malicious third parties or illegal sites created with malicious intent, malware may be downloaded without permission.
In addition to the above routes, you may be infected with malware when accessing cloud storage services or when installing software or apps. Malware can invade from any place or action, so caution is required.
4. How to Prevent Malware Infection
In order to protect your computer, smartphone, etc. from malware infection, it is important to have a basic knowledge of malware and take sufficient measures in advance.
■How to prevent malware infection/Points to consider
- Install anti-virus software (security software) and always update and set it to the latest version
- Keep your OS and apps up to date
- Do not open suspicious emails or attachments
- Do not access suspicious sites or URLs
- Encrypt important files and confidential information in case of information leakage
If you are infected with malware, you will not only suffer financial and informational damage, but you will also greatly lose the trust and credibility of your business partners and customers. In order to prevent malware infection from having a negative impact on your business, be sure to install and operate anti-virus software (security software). We recommend products that are compatible with the latest malware.
[ Comparison of 6 Typical Security Software and Points to Consider When Choosing ]
Summary
Malware is a program that illegally performs actions that are harmful to users, and there is a risk of infection damage such as ‘account hijacking’ and ‘information theft’. Understand the key points such as the type and intrusion route of malware, and implement countermeasures to protect your computer from various malware damage.
For companies and administrators who are considering introducing security measures that can also prevent malware, the cloud-based security tool ‘Exo Security’, which is highly cost-effective and easy to operate, is recommended. Utilize ‘Exo Security’, which has functions that can appropriately respond to threats such as malware, and establish a system that allows you to proceed with your work with peace of mind in terms of security. Contact globalsupport@jiran.com for more information.