What is a Spear Phishing Attack? Risks, Basic Methods, and 3 Countermeasures Explained!

In the course of implementing security measures, many people have likely heard about spear phishing attacks. Spear phishing attacks are particularly dangerous among cyber attacks and are difficult to detect, making countermeasures essential to prevent damage.
This article provides a detailed explanation of spear phishing attacks, from an overview to examples of damage, the steps involved in executing attacks, and countermeasures to prevent them. Take thorough measures to prepare for the possibility of becoming a target of a spear phishing attack.
Table of Contents
- What is a Spear Phishing Attack?
- Damage from Spear Phishing Attacks
- Differences from Spam and Phishing
- Spear Phishing Attack Methods
- Types of Spear Phishing Attacks
- The Flow of an Attack
- Countermeasures Against Spear Phishing Attacks
- Entry Point Measures to Prevent Intrusion
- Exit Measures to Prevent Damage After Intrusion
- Employee Training
- Summary
1. What is a Spear Phishing Attack?

A spear phishing attack is a type of cyber attack that steals information or damages network devices through the network. It targets specific individuals or organizations with the aim of stealing confidential information.
While government agencies and large corporations were the main targets in the past, the scope of targets has recently expanded to include local governments and small and medium-sized enterprises. Unlike most cyber attacks, which are indiscriminate, spear phishing attacks have a clear target and purpose. Because they attack specific companies using sophisticated methods, traditional anti-virus software is insufficient.
To minimize damage, it is important to combine measures to prevent intrusion, measures to detect intrusion, and measures to quickly respond upon detection.
1-1. Damage from Spear Phishing Attacks
A characteristic of spear phishing attacks is that damage can spread rapidly from minor incidents. For example, an employee may receive an email disguised as being from an acquaintance, and opening that email can lead to a virus infection and the discovery that confidential information of the entire organization has been leaked externally. It is not uncommon for corporate information to be stolen from just one email.
The following are two examples of actual incidents.
- Operation Aurora
The most famous example of a spear phishing attack, in 2009, Google and more than 30 other companies were victims of spear phishing attacks. It is said that a large amount of confidential information was stolen by infecting systems with malicious programs, mainly by exploiting vulnerabilities in Internet Explorer. Attacks that exploit such vulnerabilities are called zero-day attacks, and zero-day attacks are very troublesome because they attack in a short period of time and are difficult to prevent. - Japan Pension Service
In 2015, the Japan Pension Service was targeted by a spear phishing attack. The attack resulted in the leakage of personal information of 1.25 million pension subscribers, spreading anxiety throughout Japan. A major point of this case is that a malicious program was embedded in an email addressed to an employee. The subject of the email was also cleverly crafted, making it a malicious method that was difficult to detect.
1-2. Differences from Spam and Phishing
Spam and phishing are sometimes used as similar terms to spear phishing attacks, but they have different meanings. The differences are as follows:
- Spam
Spam refers to advertising emails that are indiscriminately and massively distributed. The fact that it does not target specific individuals differs from spear phishing attacks. - Phishing
Phishing is a technique that impersonates banks or credit card companies to induce users to visit phishing sites, with the aim of obtaining personal information and card information to commit fraud. The major difference is that this is also an indiscriminate attack.
2. Spear Phishing Attack Methods
Before taking measures against spear phishing attacks, it is necessary to understand the methods of spear phishing attacks. Attackers use all sorts of methods to launch attacks. First, understanding the typical attack methods will allow you to take applied countermeasures.
Here, we will explain the types of spear phishing attacks and the flow of attacks.
2-1. Types of Spear Phishing Attacks
There are several types of spear phishing attacks.
- Spear Phishing Email Attack
This is the most common attack method among spear phishing attacks. Because the sender is disguised as an acquaintance or business partner, the recipient opens the email without realizing it is suspicious. By downloading attachments or clicking URLs, viruses spread throughout the organization’s network. It is important for email recipients themselves to be able to distinguish suspicious emails in order to prevent spear phishing attacks. - Watering Hole Attack
A watering hole attack is a method of tampering with a website that the target company frequently visits and inducing access. When a user accesses a fake website, a virus is downloaded, making it almost impossible to detect in advance.
2-2. The Flow of an Attack
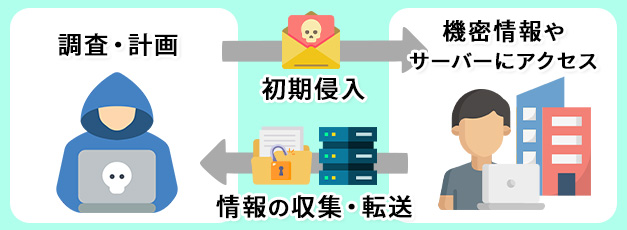
The flow until an attack is carried out is as follows:
(1) Investigation and Planning
Cyber attackers investigate the human relationships and types of software used by the targeted company. They may impersonate people involved to elicit passwords, or even rummage through trash cans, taking physical approaches. Based on the investigation results, they select the recipients of the forged emails.
(2) Initial Intrusion
They send spoofed emails to the targeted individuals. URLs and files contain malicious programs, and clicking them executes the malicious programs, infecting the system with viruses and malware. Sophisticated deception techniques are used in the sender and subject lines to avoid arousing suspicion in the recipient.
(3) Access to Confidential Information
Using the virus-infected computer as a base, they explore the company’s internal network and gradually advance the attack over time.
(4) Access to Servers
If the desired information is not found on the infected computer, they attempt to access the database containing the company’s confidential information. If the system’s vulnerabilities are exploited or administrator privileges are hijacked, intrusion may be permitted.
(5) Information Collection and Transfer
Once they obtain confidential information, they transfer the information in a way that does not reveal the unauthorized access. After the transfer is complete, they erase all log information from the intrusion, making it difficult for the target to notice.
As described above, attackers use all means to obtain company information and attempt to access confidential information. Furthermore, a characteristic is that they leave no traces after stealing information.
3. Countermeasures Against Spear Phishing Attacks

To avoid becoming a victim of a spear phishing attack, it is necessary to take thorough attack countermeasures on a regular basis. However, since it is difficult to completely prevent virus intrusion, it is important to combine measures to prevent attack intrusion and measures to prevent damage after intrusion.
The following describes entry point measures to prevent attack intrusion and exit measures to prevent damage after intrusion.
3-1. Entry Point Measures to Prevent Intrusion
To prevent virus intrusion, it is essential to use email filtering services and information security software. However, many commercially available security products are not detected, and preparations for spear phishing attacks may be insufficient.
It is also important not to open suspicious emails or software, and to regularly update the OS and software to the latest programs.
3-2. Exit Measures to Prevent Damage After Intrusion
If a virus intrudes, it is important to stop the information before it is transferred to the outside.
Utilize security software that monitors logs to quickly detect the intrusion of malicious programs.
Since malicious programs in spear phishing attacks take time to actually start attacking, monitoring logs can minimize damage.
It is also important to define information sharing and response procedures in the event of damage. System administrators should establish policies for initial response measures so that they can respond quickly when damage is reported.
3-3. Employee Training
In order to prevent damage from spear phishing attacks, it is important not only to rely on security software, but also to provide security education to employees who receive emails. Training should be conducted with examples of typical spear phishing email texts and how to deal with them if they are opened.
It is necessary to convey to employees that the actions of just one person can cause damage to the entire company.
Summary
Spear phishing attacks are cyber attacks that target specific individuals or companies. To prepare for spear phishing attacks, it is important to combine entry point measures and exit measures. It is essential to educate employees not to open suspicious emails and to update software regularly.
EXO Security provides security measures that can respond to various threats. Installing EXO Security monitors your computer in real time, preventing virus infection even if you are targeted. If you are considering preparing for spear phishing attacks, please feel free to contact us.
If you have any questions or need further assistance, please contact us at globalsupport@jiran.com.